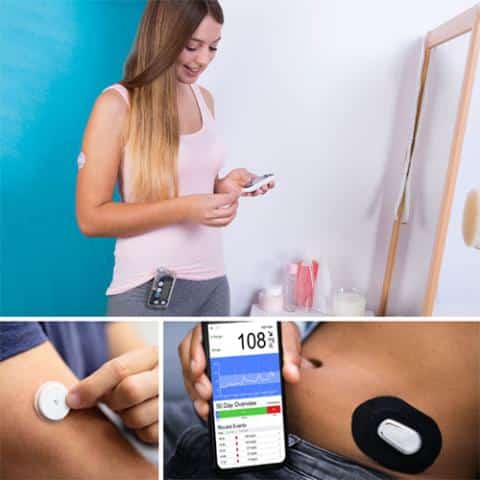
The management of blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) have become a vital tool in achieving this. Recently, the FDA approved a next-generation CGM featuring an innovative two-step insertion process, promising greater ease of use and improved accuracy. In this blog, we’ll explore what this approval means for blood sugar monitoring, how the two-step insertion process works, and the potential benefits for those managing diabetes.
Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Continuous glucose monitors are devices that measure blood sugar levels in real time, providing valuable data to help individuals manage their diabetes more effectively. Unlike traditional fingerstick monitors that require manual blood samples, CGMs use a sensor placed under the skin to track glucose levels continuously. This data is transmitted to a receiver or smartphone, allowing users to monitor their blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.
CGMs have revolutionized diabetes care by offering insights into how different foods, activities, and medications affect blood sugar levels. They enable more precise management, reduce the frequency of hypoglycemic events, and help users make informed decisions about their health.
The Next-Generation CGM: What’s New?
The FDA’s approval of the next-generation CGM marks a significant advancement in blood sugar monitoring technology. One of the most notable features of this new device is the two-step insertion process, designed to make the sensor insertion simpler, quicker, and less painful. This innovation aims to address some of the common challenges users face with traditional CGMs, such as difficulty with sensor placement and discomfort during insertion.
The two-step insertion process involves a more intuitive design that minimizes user error and enhances the overall user experience. This improvement is expected to increase the adoption of CGMs among individuals with diabetes, as it reduces the barriers associated with using the device.
More Read About: AI-Enhanced CGM Approved in Europe, Enhances Diabetes Management
How the Two-Step Insertion Process Works
The traditional insertion process for CGM sensors often involves multiple steps, including prepping the skin, inserting the sensor, and securing it in place. While effective, this process can be cumbersome and intimidating for some users, particularly those new to CGM technology.
The next-generation CGM’s two-step insertion process streamlines these steps into a more user-friendly experience. Here’s how it works:
Preparation
The first step involves preparing the insertion site. This may include cleaning the skin and applying an adhesive patch to secure the sensor. The preparation step ensures that the sensor stays in place and functions accurately.
Insertion
The second step involves the actual insertion of the sensor. The new design simplifies this process, requiring less manual dexterity and reducing the likelihood of incorrect placement. The sensor is inserted with a single motion, minimizing discomfort and making the experience more comfortable for users.
This two-step process is expected to be particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle with the more complex insertion procedures of earlier CGM models. By reducing the learning curve and discomfort, the new CGM could encourage more consistent use, leading to better blood sugar management.
Benefits of the Next-Generation CGM
The next-generation CGM offers several potential benefits for blood sugar management, particularly with its enhanced insertion process. These benefits include:
Improved Accuracy
With more consistent and accurate sensor placement, users can expect improved accuracy in blood sugar readings. Accurate readings are crucial for making informed decisions about insulin dosing, dietary choices, and other aspects of diabetes management.
Increased Comfort
The two-step insertion process is designed to be less painful and more comfortable, encouraging regular use of the CGM. For many users, the discomfort associated with sensor insertion has been a barrier to consistent use. By addressing this issue, the next-generation CGM promotes better adherence to glucose monitoring.
Reduced User Error
The simplified insertion process reduces the chances of user error, which can lead to inaccurate readings or sensor malfunctions. This improvement is particularly important for new users who may be unfamiliar with CGM technology.
Greater Accessibility
By making the CGM easier to use, the next-generation device could become more accessible to a broader range of individuals with diabetes. Whether someone is newly diagnosed or has been managing diabetes for years, the simplified process makes CGM technology more approachable.
Impact on Diabetes Management
The FDA’s approval of the next-generation CGM with a two-step insertion process has the potential to significantly impact diabetes management. As more individuals adopt this technology, we may see a shift in how blood sugar levels are monitored and managed. The combination of improved accuracy, comfort, and ease of use could lead to better overall health outcomes for those with diabetes.
For healthcare providers, the new CGM offers an additional tool to support patients in managing their blood sugar levels. The enhanced accuracy and user-friendly design make it easier for patients to adhere to monitoring recommendations, leading to more effective treatment plans and fewer complications related to diabetes.
Conclusion
The FDA’s approval of the next-generation CGM with a two-step insertion process represents a major advancement in blood sugar monitoring technology. By simplifying the insertion process and improving user experience, this new device has the potential to revolutionize diabetes care and help individuals better manage their blood sugar levels.
As the technology becomes more widely available, more people with diabetes will likely embrace CGMs as an essential part of their health management routine. The improved accuracy, comfort, and ease of use offered by the next-generation CGM can lead to better health outcomes, making it a valuable tool in the ongoing fight against diabetes.