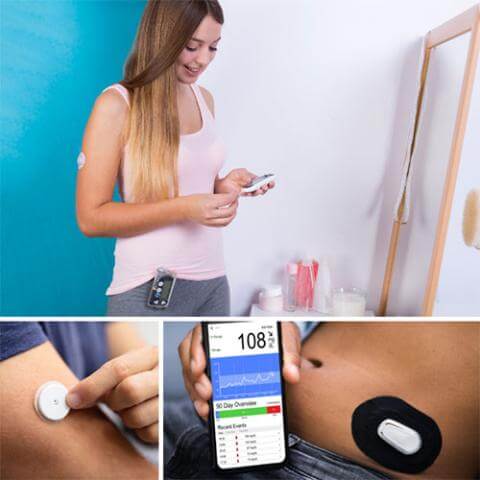
The field of diabetes care is undergoing a significant transformation with the introduction of innovative continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems. These cutting-edge technologies are designed to provide real-time insights into blood glucose levels, offering a more comprehensive approach to managing diabetes. This blog explores the latest advancements in CGM systems, their potential to revolutionize diabetes care, and the implications for patients and healthcare providers alike.
The Evolution of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring has come a long way since its inception. Early systems were cumbersome and required frequent calibration, making them less user-friendly. However, recent advancements have led to the development of more sophisticated CGM systems that offer improved accuracy, ease of use, and integration with other health technologies.
Advances in Technology
The new generation of CGM systems boasts several key advancements that are set to transform diabetes care:
Enhanced Accuracy:
Modern CGMs provide more precise readings, reducing the risk of false alarms and improving overall glucose management.
User-Friendly Design:
Recent models are designed for ease of use, with features like wireless data transmission and seamless integration with smartphones and smartwatches.
Extended Wear Time:
Improved sensors allow for longer wear periods, minimizing the frequency of replacements and reducing patient discomfort.
Impact on Diabetes Care
The integration of advanced CGM systems into routine diabetes care offers numerous benefits for both patients and healthcare providers.
Real-Time Monitoring
One of the most significant advantages of the new CGM systems is the ability to monitor blood glucose levels in real-time. This continuous stream of data enables patients to make immediate adjustments to their diet, medication, and lifestyle, leading to better glucose control and overall health.
More Read About: Continuous Glucose Monitoring for the Masses: Are We Ready for It?
Personalized Treatment Plans
With access to detailed glucose data, healthcare providers can create more personalized treatment plans. The ability to analyze trends and patterns in glucose levels allows for more accurate adjustments to insulin doses and other aspects of diabetes management.
Reduced Complications
Effective glucose control is crucial for preventing complications associated with diabetes, such as neuropathy, retinopathy, and cardiovascular issues. By providing real-time data and enabling more precise management, CGM systems contribute to reducing the risk of these complications.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of the new CGM systems are clear, there are also some challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Cost
The expense of the new CGM systems is one of the main issues. These advanced devices can be expensive, and not all insurance plans may cover them. This could limit accessibility for some patients.
Learning Curve
There’s always a learning curve associated with the introduction of new technologies. Patients and healthcare providers may need time to become accustomed to the features and functionalities of the new CGM systems.
Data Management
With the influx of continuous glucose data, managing and interpreting this information can be overwhelming. Patients and providers will need to develop strategies for effectively using the data to make informed decisions.
The Future of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
The future of continuous glucose monitoring holds exciting possibilities for diabetes care. As technology continues to advance, we can expect further improvements in accuracy, convenience, and integration with other health technologies.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
Emerging AI technologies are being integrated into CGM systems to provide even more personalized insights. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of data to predict trends and offer recommendations for managing glucose levels.
Enhanced Connectivity
Future CGM systems are likely to feature enhanced connectivity options, allowing for seamless integration with other health devices and platforms. This will enable a more holistic approach to diabetes care.
Broader Accessibility
Efforts are underway to make advanced CGM systems more affordable and accessible to a broader range of patients. As technology becomes more widespread and insurance coverage improves, more individuals will benefit from these transformative tools.
Conclusion
The new continuous glucose monitoring systems represent a significant advancement in diabetes care. By offering real-time insights, personalized treatment options, and improved glucose control, these technologies have the potential to transform the management of diabetes. While there are challenges to overcome, the future of CGM systems looks promising, with continued advancements and broader accessibility on the horizon. As we embrace these innovations, we move closer to a future where diabetes care is more effective and patient-centered than ever before.