It’s a daily struggle for Americans with type 1 diabetes to control their blood sugar levels. Insulin pumps, continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and related supplies provide substantial improvements in the treatment of diabetes. The US healthcare system, however, offers a challenging environment for obtaining these technologies, in contrast to several other industrialized countries. This essay explores the variables driving access and potential solutions as it digs into the most recent data on CGM, insulin pumps, and consumable procurement in the US.
Continuous Glucose Monitors
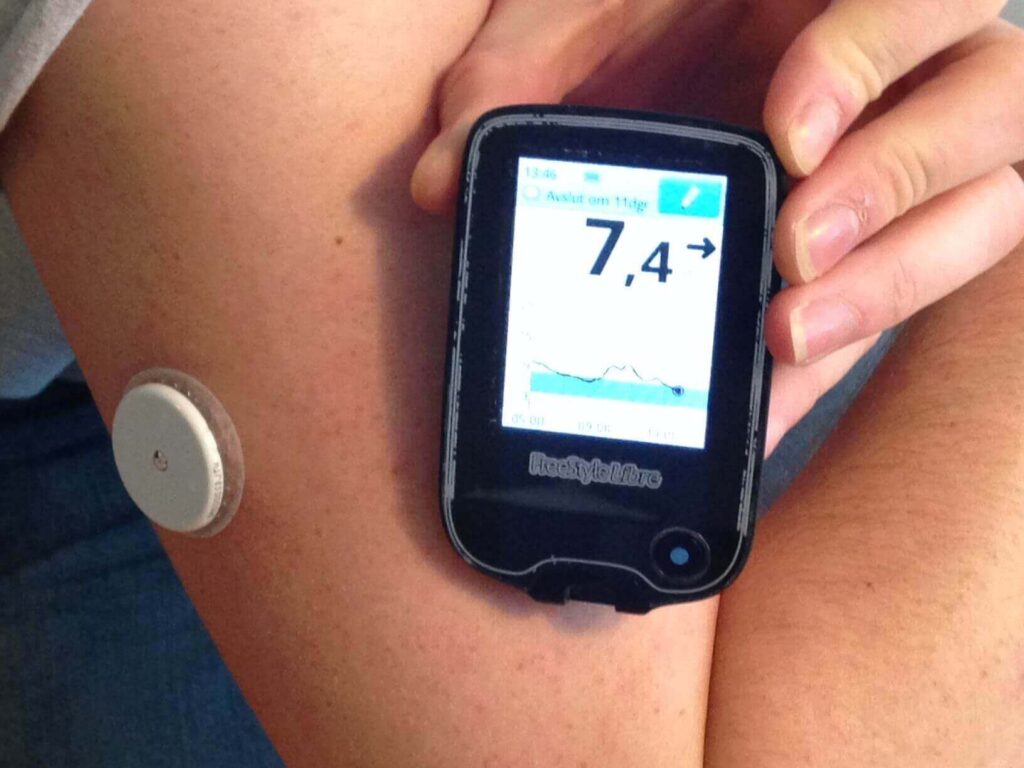
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) use a sensor that is implanted under the skin to deliver real-time blood glucose information. This continuous data stream provides a more complete picture of glucose changes than conventional finger pricking. This makes it possible to improve glycemic control and make better modifications to insulin therapy.
Landscape of Procurement
The US healthcare system is primarily dependent on private insurance, and there are wide variations in the policies that cover Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs). Below is a summary of important variables:
Insurance Coverage
The majority of significant insurance providers offer CGM coverage, however, specifics could vary. Access may be impacted by variables such as prior authorization requirements, deductible reached, and policy tier. Coverage is frequently conditioned on proving a history of regular blood sugar monitoring or having problems with conventional techniques.
Extra-Pocket Expenses
Patients may have to pay a large amount out of cash for Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) even if they have insurance. Deductibles, copays, and costs for sensors, transmitters, and other supplies are a few examples of these. The regular replacement of sensors, which happens every 7 to 14 days, might add significantly to the continuing costs.
Insulin Pumps
Insulin can be delivered precisely and subtly throughout the day with insulin pumps. They are set up to receive boluses, or extra insulin for meals, and basal rates, or background insulin. Compared to several daily injections, pumps offer more flexibility and maybe better glycemic management (MDI).
Landscape of Procurement:
Access to insulin pumps is dependent on insurance coverage, the same as with Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs):
Insurance Coverage
Insulin pumps are generally covered by insurance policies, however, the specifics differ. Important things to think about are co-pay levels, covered pump models, and prior permission requirements. Additionally, before authorizing pump therapy, certain plans could demand an MDI trial period.
Out-of-Pocket Charges
In addition to the initial cost of the pump, patients may have to pay co-pays for supplies like reservoirs and infusion sets. They may also incur out-of-pocket charges for possible pump usage training.
Insulin Pump Replacement Parts:
Consumables like infusion sets, catheters, and reservoirs are necessary for the operation of the pump. Regular replacement is necessary to ensure optimal delivery and sterility.
Landscape of Procurement
Insurance Coverage
Most insurance policies that cover insulin pumps also cover consumables. But it’s important to pay close attention to specifics like co-pays, frequency restrictions, and prior authorization requirements.
Out-of-Pocket Costs
Co-pays may be a part of the continuing expenses for necessary pump supplies even if they are reimbursed by insurance.
Factors Influencing US Procurement
Cost
For both patients and insurers, cost is a key motivator in the US healthcare system. Insulin pumps and Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) are expensive purchases. Affordability may be impacted by negotiations with device makers and the availability of generic consumables.
Insurance Coverage Complexity
Many patients find it difficult to navigate the complex world of insurance plans due to their variable levels of coverage and out-of-pocket expenses. Comprehending the specifics of each plan is essential.
Prior Authorization
Before receiving a CGM or pump, it can be necessary to acquire prior authorization from an insurance. This can be a time-consuming and irritating process that delays access to these essential devices.
Possible Remedies
Enhanced Insurance Transparency
Patients can be considerably more empowered to navigate the procurement process if insurance companies communicate more clearly about the coverage details for CGMs, pumps, and consumables.
Standardized Prior Authorization
It is possible to cut down on delays and guarantee timely access by implementing streamlined prior authorization procedures that take into account evidence-based standards.
Cost Assistance Programs
Financial support for CGMs, pumps, and consumables can be provided via initiatives from device makers, patient advocacy groups, and nonprofits.
Put Value-Based Care First
Because value-based care models base financing decisions on long-term health outcomes, they may encourage wider use of CGM and pump usage because of the potential cost savings associated with better glucose control.
Explore More Continuous Glucose Monitors Evolution: US Market Leadership and Global Outlook
The Future of Acquisition
Technological Advancements
Procurement procedures may need to be modified to make room for new features and pricing structures as CGM and pump technology advances with features like closed-loop systems for automated insulin delivery.
Policy Changes
Access to these technologies may be enhanced by prospective legislative or regulatory measures intended to standardize and increase transparency in insurance coverage.
Extra Things to Think About When Purchasing CGM, Pumps, and Consumables in the US
In addition to the primary causes and possible remedies mentioned, the following other factors may also have an impact on the US market for CGM, insulin pumps, and consumables:
Patient Support and Education
Understanding Insurance
Patients can be better able to speak up for themselves if they are given the information and skills necessary to understand the basics of their insurance plan, including coverage details, out-of-pocket expenses, and appeals procedures.
Training and Support
To guarantee proper use and optimize the benefits, switching to Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) or pumps frequently necessitates thorough training. Support initiatives may be essential for long-term management success.
telemedicine:
The emergence of telehealth presents opportunities for better access to discussions with diabetes educators and medical specialists, expediting the prescription-gathering and CGM or pump therapy management processes.
Technological Progress
Continuous Innovation
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) may provide longer wear times with higher accuracy as sensor technology advances, thereby lowering expenses related to frequent sensor changes.
Interoperability
Better communication between Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs), pumps, and other diabetes care instruments may make data collecting easier and offer a more comprehensive picture of blood glucose levels, which may lead to better treatment choices.
Studies on Cost-Effectiveness
Collecting Evidence
Research showing the CGM and pump’s long-term cost-effectiveness, especially in averting complications from uncontrolled diabetes, can be crucial in persuading insurers of the benefits.
Results for Patients
Showcasing the enhanced standard of living and decreased healthcare expenses linked to efficient diabetes control accomplished by CGMs and pumps will bolster the argument for expanded availability even further.
The Function of Public Health Initiatives and Employers
Employer-Sponsored Insurance
Employer-sponsored health plans that provide full coverage for Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs), pumps, and consumables are something that employers who employ a sizable number of people with diabetes can do a great deal to support.
Public Health Initiatives
Patients’ affordability may be greatly impacted by government efforts to increase access to reasonably priced diabetes control tools, possibly through co-pay assistance programs or subsidies.
Stakeholders such as patients, healthcare providers, device manufacturers, insurers, and politicians can collaborate to provide a more fair and cost-effective environment for the procurement of CGM, insulin pumps, and consumables in the US by taking these extra factors into account. By working together, we can make sure that everyone who needs these life-changing technologies can get them.