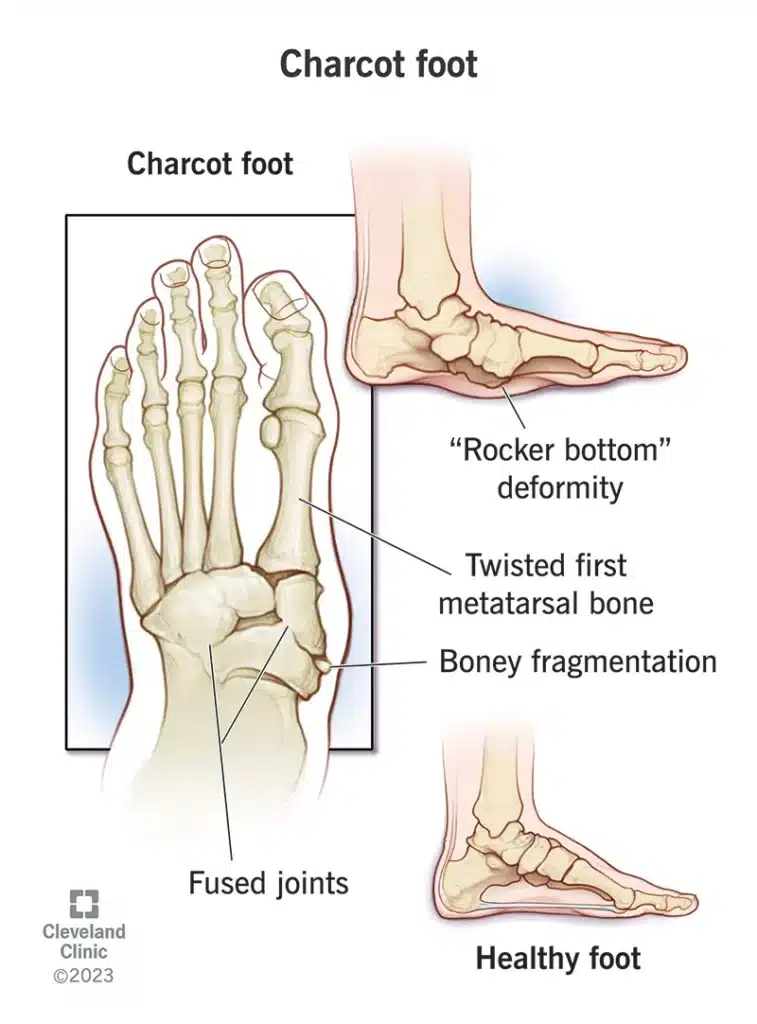
Understanding Charcot Neuroarthropathy
Charcot neuroarthropathy, commonly known as Charcot’s foot, is a severe complication associated with diabetes. This condition stems from nerve damage, often a consequence of prolonged high blood sugar levels, leading to significant damage to the bones and joints, primarily affecting the feet.
Tip: Please fill out the form if you or a friend would like more information on CGM devices.
The Diabetic Link
The correlation between Charcot neuroarthropathy and diabetes lies in the complications arising from peripheral neuropathy, a common occurrence in individuals with diabetes.
Peripheral neuropathy results in diminished sensation in the feet, making it challenging for those affected to notice injuries or stress in this area. Consequently, an injury goes unnoticed, and the individual continues to walk or bear weight on the affected foot, exacerbating the damage.
The Unfolding Process
The progression of Charcot neuroarthropathy involves a scenario where someone with diabetes sustains an injury, like stepping on a sharp object. Typically, pain would alert a person to alleviate the pressure on the injured area.
However, in the absence of pain perception associated with Charcot neuroarthropathy, the individual continues to walk, unwittingly applying pressure to the already-injured foot. This continual stress leads to fractures and dislocations, worsening the condition.
Must Read CGMs in noncritical care hospitals optimizes glycemic control
A Cascade of Effects
The intricate interplay between diabetes and Charcot neuroarthropathy initiates a series of events. Elevated blood sugar levels cause nerve damage, reducing sensation in the feet. This reduced sensation results in unnoticed injuries or stress, causing fractures and dislocations.
As these injuries remain undetected, individuals inadvertently continue to put weight on the affected foot, compounding the damage.
Identification and Management
Early identification of Charcot neuroarthropathy is pivotal. Any unexplained redness, swelling, or warmth in the foot, especially in individuals with diabetes, warrants immediate attention. Diagnosis involves a thorough clinical evaluation and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to assess the extent of bone and joint involvement.
Read Guide about Wegovy Dosage Guide: The Best Way For Weight Loss
Preventive Measures
Prevention forms a cornerstone in managing Charcot neuroarthropathy. Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels, regular foot examinations, appropriate footwear, and measures to reduce pressure on the feet are vital. Early intervention, such as offloading the affected area using braces or casts, is crucial for effective treatment.
Also, read about America’s Diabetes Crisis
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between Charcot neuroarthropathy and diabetes is crucial in managing this potentially debilitating condition. Recognizing the interplay between high blood sugar levels, nerve damage, and foot complications enables early identification and intervention.
By adopting proactive measures and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with Charcot neuroarthropathy, significantly enhancing their quality of life.