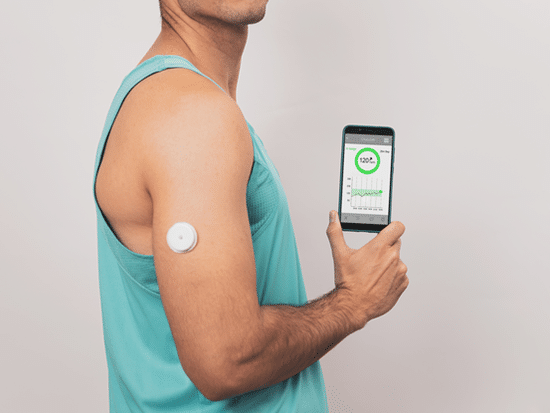
In the world of diabetes management, Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) have emerged as a groundbreaking tool. These devices offer a real-time view of glucose levels, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. But why should someone with diabetes consider wearing a CGM? In this blog, we explore the reasons behind the growing popularity of CGMs and how they can enhance diabetes care.
The Basics of Continuous Glucose Monitors
A Continuous Glucose Monitor is a small device that tracks glucose levels throughout the day and night. Unlike traditional fingerstick tests that provide a single reading, Continuous Glucose Monitors continuously measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid—the fluid between cells. This data is transmitted to a receiver or smartphone app, giving users a comprehensive picture of their glucose trends.
Why Wear a Continuous Glucose Monitor?
The decision to wear a Continuous Glucose Monitor can be life-changing for those managing diabetes. Here are some compelling reasons why more and more individuals are turning to CGMs as a critical component of their diabetes care.
Real-Time Glucose Monitoring
One of the most significant advantages of wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor is the ability to monitor glucose levels in real-time. This feature is especially beneficial for people with diabetes who need to keep their glucose levels within a specific range. Unlike traditional methods that require intermittent testing, a CGM provides constant feedback, allowing users to see how their glucose levels fluctuate in response to various factors such as food, exercise, and stress.
More Read About: CGM Use Grows in Primary Care for Diabetes Management
Real-time monitoring can also alert users to potential issues before they become severe. For instance, if glucose levels are trending too high or too low, the Continuous Glucose Monitors can provide an alert, enabling the user to take corrective action. This proactive approach to diabetes management can help prevent dangerous episodes of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Better Understanding of Glucose Patterns
Wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor allows individuals to gain a deeper understanding of their glucose patterns. Over time, the data collected by the CGM can reveal trends and patterns that may not be apparent through occasional fingerstick tests. For example, a person might notice that their glucose levels consistently rise after eating certain foods or drop during specific times of the day.
This insight can lead to more informed decisions about lifestyle choices and diabetes management strategies. By identifying and addressing factors that cause glucose fluctuations, individuals can achieve better overall glucose control, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Improved HbA1c Levels
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) is a critical marker of long-term glucose control in people with diabetes. Studies have shown that wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor can lead to significant improvements in HbA1c levels. This is because CGMs help users maintain more stable glucose levels, reducing the frequency and severity of both high and low blood sugar episodes.
Lower HbA1c levels are associated with a reduced risk of diabetes-related complications, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. For many individuals, the prospect of improving their HbA1c levels is a compelling reason to wear Continuous Glucose Monitors.
Enhanced Quality of Life
Managing diabetes can be challenging and stressful, particularly when it comes to monitoring glucose levels. The need for frequent fingerstick tests can be inconvenient and uncomfortable, leading some individuals to avoid testing as often as they should. Wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor can alleviate some of this burden by providing continuous, non-invasive glucose monitoring.
This convenience can lead to an enhanced quality of life. With Continuous Glucose Monitors, individuals no longer need to perform as many fingerstick tests, freeing them from the discomfort and hassle of traditional glucose monitoring. Additionally, the peace of mind that comes from knowing one’s glucose levels at all times can reduce anxiety and improve overall well-being.
Personalized Diabetes Management
One of the most powerful benefits of wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor is the ability to personalize diabetes management. The data collected by a CGM allows individuals to tailor their treatment plans to their specific needs, leading to more effective and individualized care.
For instance, someone may discover that they need to adjust their insulin dosage based on their glucose patterns or that they respond better to certain foods or exercise routines. This level of personalization can lead to more successful diabetes management, as individuals are better equipped to make decisions that suit their unique circumstances.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor are clear, there are some challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Cost and Insurance Coverage
One of the primary barriers to CGM use is cost. Continuous Glucose Monitors can be expensive, and not all insurance plans cover them. It’s important for individuals considering Continuous Glucose Monitors to check with their insurance provider to determine coverage and explore any available financial assistance options.
Learning Curve
There can be a learning curve when starting with a Continuous Glucose Monitor. Users need to become familiar with the device, understand how to interpret the data, and know how to respond to alerts. However, most people find that the benefits far outweigh the initial challenges, and many resources are available to help with the transition.
Device Maintenance
Wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor requires regular maintenance, such as changing the sensor every few days and ensuring the device is calibrated correctly. While these tasks are generally straightforward, they do require some time and attention. However, the effort is minimal compared to the convenience and insights provided by the Continuous Glucose Monitors.
Conclusion
Wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor offers numerous benefits for those managing diabetes. From real-time monitoring and a better understanding of glucose patterns to improved HbA1c levels and enhanced quality of life, CGMs have become an essential tool in modern diabetes management. While there are challenges to consider, the advantages of Continuous Glucose Monitors make them a worthwhile investment for many individuals.
As technology continues to advance, the role of Continuous Glucose Monitors in diabetes management is likely to expand even further, offering new opportunities for people with diabetes to take control of their health and improve their outcomes.